Junta YANAI
Professor
Laboratory of Soil Chemistry,
Graduate School of Life and Environmental Sciences,
Kyoto Prefectural University
1-5, Shimogamo Hangi-cho, Sakyo,
Kyoto 606-8522, Japan
Phone: +81-75-703-5649 E-mail: yanai@kpu.ac.jp
URL: http://www2.kpu.ac.jp/life_environ/bioanal_chem/yanai.html
【 Proposal for collaborative research is welcome ! 】
![]()
Research
Theme:
-Evaluation of fertility
status and quality of soils and establishment of sustainable soil management
based on the analysis of soil-plant relationship-
Soil is essential for our life as it is the basis for sustainable agricultural production and the terrestrial environment. To conserve indispensable soil resource is, therefore, directly related to our well-being. Main theme of my research is to evaluate fertility status and quality of soils and to establish sustainable soil management based on the analysis of soil-plant relationship. For this main theme, specific research topics were set up including 1) evaluation and management of fertility status and quality of agricultural soils in Japan based on the measurement of total and available fractions of plant essential elements in soils, 2) fertility reevaluation of paddy soils in tropical Asia after 50 years of the introduction of “Green Revolution”, 3) evaluation of biogeochemical cycling of nutritional elements in agricultural ecosystems and proposal of sustainable soil/land management in the tropics and dry regions, 4) analysis of the mechanisms of soil nutrient supply in the rooting zone and in the rhizosphere and proposal of evaluation methods of soil fertility, 5) elucidation of the mechanism of sorption/desorption process of radiocesium (RCs) in soils and establishment of countermeasures to reduce the risk of transfer of RCs from soil to plant, 6) elucidation of the mechanism of soil pollution with heavy metals and establishment of remediation strategies for heavy metal polluted soils and 7) spatial variability analysis of soil characteristics and proposal of site-specific soil management and rational soil sampling scheme. Through the research on these topics, I wish to propose rational measures to maintain and improve soil productivity and soil quality, which, I believe, contribute to rational use of soil resources and finally to the conservation of global environment.
1.Evaluation and Management of Fertility
Status and Quality of Agricultural Soils in Japan based on the Measurement of Total
and Available Fractions of Plant Essential Elements in Soils
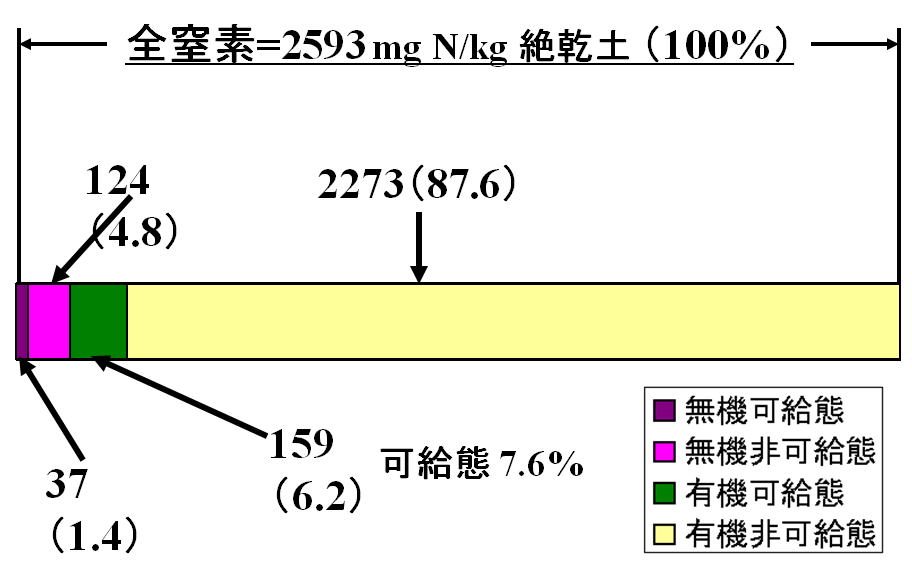
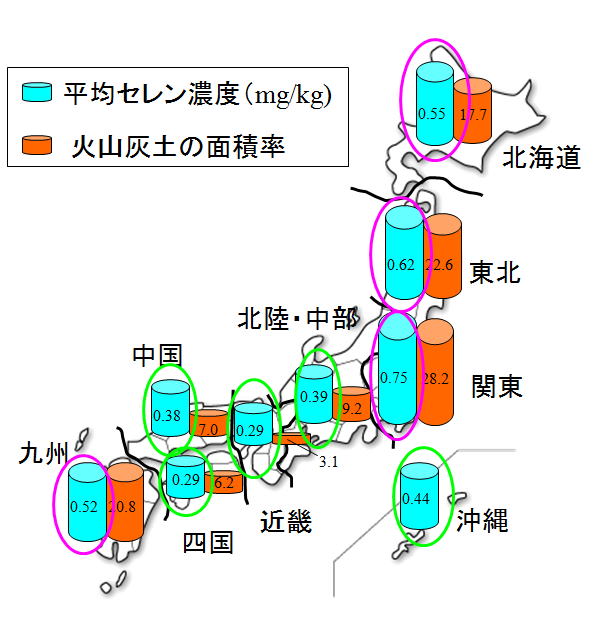
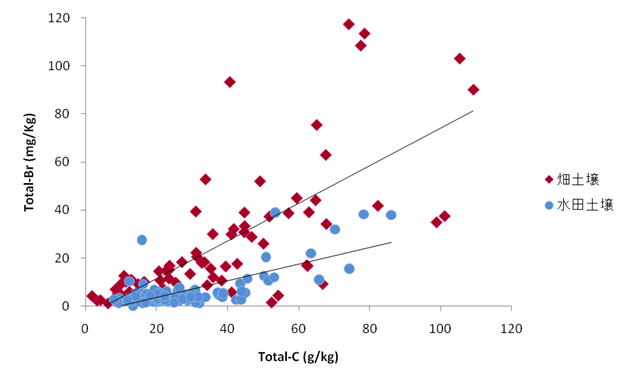
Comprehensive analysis of
total amount and chemical fractions of elements in soils is essential not only
for 1) fertility evaluation of the soils but also for 2) soil quality
evaluation and 3) estimation of the impact of soil factors for human health
through food chain. Based on this
background, we have analyzed total and available fractions of elements (including
plant essential nutrients) of 180 soil samples collected from agricultural
fields all over Japan. This research can
offer basic information for food production and environmental conservation in
Japan and for understanding of biogeochemical cycling of elements by the
comparison with the data on the elemental composition of rocks and river
waters. In addition, this research will enable to understand the relative situation
of agricultural soils in Japan in comparison with those in Asia.
2.Fertility ReEvaluation of Paddy Soils in Tropical Asia after 50 years of the introduction of “Green Revolution” (FREPS 50 Project)
Rice yield in tropical Asia has been increasing since the introduction of “Green Revolution” in 1960s but the effect of the increased fertilizer application and increased removal of rice grains for the past 50 years on soil fertility status has not been comprehensively evaluated. Fortunately, the data on fertility status of paddy soils in tropical Asia about 50 years ago is available because Kawaguchi and Kyuma (1977) investigated fertility status of the paddy soils from 10 countries in tropical Asia in 1960s. The objectives of this research are 1) to collect paddy soil samples in 2010s at locations where Kawaguchi & Kyuma collected their samples, 2) to evaluate the changes of fertility status of paddy soils in the past 50 years by comparing the data at present with those in 1960s and 3) to propose rational and sustainable management of paddy soils in tropical Asia for the coming dacades. At present, research on paddy soils in Thailand, Philippine, Malaysia and Bangladesh are in progress.







3.Evaluation of Biogeochemical Cycling of Nutritional Elements in Agricultural Ecosystems and Proposal of Sustainable Soil/Land Management in the Tropics and Dry Regions
Agricultural ecosystems in the tropics and dry regions are often vulnerable
to degradation due to inherently low soil fertility as well as over-burden due to recent increase
of human population and agricultural intensification. In order to control soil degradation and to offer sustainable soil/land management strategies, biogeochemical cycling of nutritional elements in agricultural systems
has been evaluated in relation to a variety of soil/land management, in many countries such as Thailand, Kazakhstan, Indonesia and Philippines.




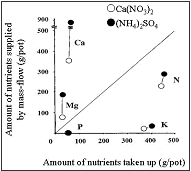
For the nutritional elements such and N, P, K and micronutrients, mechanisms of nutrient supply in the rooting zone and in the rhizosphere (the interface between soil and root) have been investigated by taking account of chemical and positional availability of the nutrients. Based on the findings, re-evaluation of conventional evaluation methods of soil fertility and establishment of new evaluation methods of soil fertility have been carried out. Especially temporal and spatial changes of soil fertility status in the rooting zone and in the rhizosphere in accordance with plant growth have been intensively investigated by the measurement of soil solution composition, fractionation of soil solid phase and mass-flow/diffusion concept for the movement of nutrients in soils, in combination with looped hollow fiber soil solution sampler and rhizobox techniques.


5.Elucidation of the Mechanism of Sorption/Desorption
Process of RadioCesium (RCs) in Soils and Establishment of Countermeasures to
Reduce the Risk of Transfer of RCs from Soil to Plant
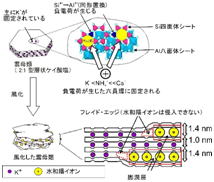
Radiocecium (RCs) is known to be strongly fixed in the “frayed edge zone”
of micaceous minerals in soils. The relationship between the type, amount
and/or degree of weathering of micaceous minerals and RCs adsorption potential
of soils is not fully understood. The
objective of this research is to elucidate mineralogical factors controlling
the mobility of RCs in soil, by analyzing the effect of type, amount, degree of
weathering of micaceous minerals and modification of such minerals with organic
matter and Al-polymers in soil on RCs adsorption potential of the soils. The relationship between RCs adsorption
potential and transfer factor from soil to plant is also investigated using
soils with a variety of mineralogical and chemical characteristics. Furthermore, the effect of aeolian dust on
RCs adsorption potential of Japanese soils is also under investigation to
clarify the potential source of micaceous minerals.




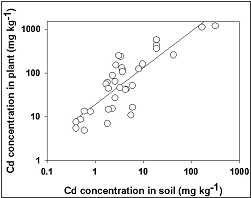
In order to remediate agricultural soils polluted with heavy metals, research
on phytoremediation of Cd-contaminated soils using a Cd hyperaccumulator plant has been carried
out. Namely the effect of soil characteristics on the efficiency of remediation using a Brassica species (Thlaspi caerulescens) has been investigated for a range soils with a variety of Cd levels. In addition, evaluation methods and rational soil management practices have been proposed for a wide range of soils.

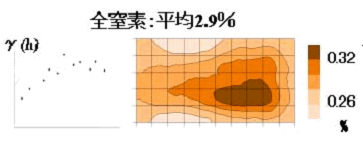
7.Spatial Variability Analysis of Soil Characteristics
and Proposal of Site-Specific Soil Management and Rational Soil Sampling Scheme
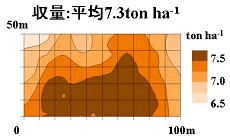
Spatial variability analysis of soil characteristics and yield of rice was
carried out using geostatistics and the merit of site-specific management or
“precision agriculture” in paddy rice production was quantitatively
investigated. The analysis of data of
temporally and spatially collected paddy soil samples was carried out to
investigate the relationship between sampling number or sampling frequency and
the reliability of the data and to propose rational soil sampling scheme for
paddy soils. In addition, spatial
variability analysis of soil characteristics and emission rate of global
warming gasses (such as N2O and CO2) was also carried out to propose rational measurement strategy as well
as rational management strategy to reduce the emission of such gasses.


![]()
+ Japanese Society of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition (Council member: 2013-present; Editor of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition: 1996-1997, 2001-2002, 2011-2014; Editor of Japanese Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition: 2005-2006, 2016-2017)
+ Japanese Society of Pedology (Council member: 2016-present; Editor of Pedologist Journal: 2004-2005)
+ International Union of Soil Science
+ Soil Science Society of America
+ British Society of Soil Science
+ Japanese Society of Tropical Agriculture
+ Japanese Society of Analytical Chemistry
Education:
+ Mar-1990: Bachelor of Agriculture (Agricultural Chemistry), Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan
+ Mar-1992: Master of Agriculture (Agricultural Chemistry), Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan
+ Apr-1993 to Jan-1994: Visiting student to Scottish Crop Research Institute, UK
+ Mar-1998: Doctor of Agriculture (Soil Science), Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan
Professional Experience:
+ Jul-1995 to Mar-2005: Assistant Professor, Graduate School of Agriculture and Graduate School of Global Environmental Studies, Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan
+ Aug-2002 to Aug-2003: Visiting Scientist (supported by Japanese Society for Promotion of Science (JSPS)), Rothamsted Research, UK
+ Apr-2005 to Mar-2011: Associate Professor, Graduate School of Life and Environmental Sciences, Kyoto Prefectural University, Kyoto, Japan
+ Apr-2011 to present: Professor, Graduate School of Life and Environmental Sciences, Kyoto Prefectural University, Kyoto, Japan
Award Received:
+ Apr-2006: Encouragement Award of Japanese Society of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition
+ Apr-2006: Best Paper Award of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition
Publications - Refereed International Journals:
1. Yanai, J., Araki, S. and Kyuma, K. 1993: Use of a looped hollow fiber sampler as a device for nondestructive soil solution sampling from the heterogeneous root zone. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 39, 737-743.
2. Yanai, J., Araki, S. and Kyuma, K. 1995: Effects of plant growth on the dynamics of the soil solution composition in the root zone of maize in four Japanese soils. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 41, 195-206.
3. Yanai, J., Linehan, D.J., Robinson, D., Young, I.M., Hackett, C.A., Kyuma, K. and Kosaki, T. 1996: Effects of inorganic nitrogen application on the dynamics of the soil solution composition in the root zone of maize. Plant and Soil, 180, 1-9.
4. Yanai, J., Nakano, A., Kyuma, K. and Kosaki, T. 1997: Application effects of controlled-availability fertilizer on dynamics of soil solution composition. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 61, 1781-1786.
5. Tsunekawa, A., Kar, A., Yanai, J., Tanaka, U. and Miyazaki, T. 1997: Influence of continuous cultivation on the soil properties affecting crop productivity in the Thar Desert, India. Journal of Arid Environment, 36, 367-384.
6. Yanai, J., Robinson, D., Young, I.M., Kyuma, K. and Kosaki, T. 1998: Effects of the chemical form of inorganic nitrogen fertilizers on the dynamics of soil solution composition and on nutrient uptake by wheat. Plant and Soil, 202, 263-270.
7. Yanai, J., Yabutani, M., Kang, Y., Huang, B., Luo, G. and Kosaki, T. 1998: Heavy metal pollution of agricultural soils and sediments in Liaoning Province, China. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 44, 367-375.
8. Moritsuka, N., Yanai, J., and Kosaki, T. 2000: Effect of plant growth on the distribution and forms of soil nutrients in the rhizosphere. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 46, 439-447.
9. Yanai, J., Lee, C.K., Umeda, M. and Kosaki, T. 2000: Spatial variability of soil chemical properties in a paddy field. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 46, 473-482.
10. Moritsuka, N., Yanai, J., and Kosaki, T. 2000: Non-destructive method for determining temporal and spatial changes of the soil solution chemistry in the rhizosphere. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 46, 713-719.
11. Moritsuka, N., Yanai, J., and Kosaki, T. 2001: Effect of application of inorganic and organic fertilizers on the dynamics of soil nutrients in the rhizosphere. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition 47, 139-148.
12. Yanai, J., Lee, C.K., Kaho, T., Iida, M., Matsui, T., Umeda, M. and Kosaki, T. 2001: Geostatistical analysis of soil chemical properties and rice yield in a paddy field and application to the analysis of yield-determining factors. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 47, 291-301.
13. Moritsuka, N., Yanai, J., and Kosaki, T. 2001: Effect of soil heating on the dynamics of soil available nutrients in the rhizosphere. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 47, 323-331.
14. Moritsuka, N., Yanai, J., and Kosaki, T. 2002: A sensitive method for detecting the depletion of nonexchangeable potassium in the rhizosphere using a sequential extraction with 0.01 molar hydrochloric acid. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 48, 577-583.
15. Yamamuro, S., Ueno, H., Yamada, H., Takahashi, Y., Shiga, Y., Miyahara, S., Shimonihara, T., Murase, J., Yanai, J. and Nishida, M. 2002: Uptake of carbon and nitrogen through roots of rice and corn plants, grown in soils treated with 13C and 15N dual-labeled cattle manure compost. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 48, 787-795.
16. Moritsuka, N., Yanai, J., Sano, S., Fujii, A. and Kosaki, T. 2003: Evaluation of readily available nonexchangeable potassium in soil by sequential extractions with 0.01 molar hydrochloric acid. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 49, 631-639.
17. Yanai, J., Sawamoto, T., Oe, T., Kusa, K., Yamakawa, K., Sakamoto, K., Naganawa, T., Inubushi, K., Hatano, R. and Kosaki, T. 2003: Spatial variability of nitrous oxide emissions and their soil-related determining factors in an agricultural field. Journal of Environmental Quality, 32, 1965-1977.
18. Moritsuka, N., Yanai, J. and Kosaki, T. 2004: Possible processes releasing nonexchangeable potassium from the rhizosphere of maize. Plant and Soil, 258, 261-268.
19. Moritsuka, N., Yanai, J. Mori, K. and Kosaki, T. 2004: Biotic and abiotic processes of nitrogen immobilization in the soil-residue interface. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 36, 1141-1148.
20. Yanai, J., Mabuchi, N., Moritsuka, N., and Kosaki, T. 2004: Distribution and forms of cadmium in the rhizosphere of Brassica juncea in Cd contaminated soils and implications for phytoremediation. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 50, 423-430.
21. Sano, S., Yanai, J. and Kosaki, T. 2004: Evaluation of soil nitrogen status in Japanese agricultural lands with reference to land use and soil types. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 50, 501-510.
22. Moritsuka, N., Yanai, J., Umeda, M. and Kosaki, T. 2004: Spatial relationships among different forms of soil nutrients in a paddy field. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 50, 565-573.
23. Yanai, J., Mishima, A., Funakawa, S., Akshalov, K. and Kosaki, T. 2005: Spatial variability of organic matter dynamics in the semi-arid croplands of northern Kazakhstan. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 51, 261-269.
24. Nishiyama, Y., Yanai, J. and Kosaki, T. 2005: Potential of Thlaspi caerulescens for cadmium phytoremediation: comparison of two representative soil types in Japan under different planting frequencies. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 51, 827-834.
25. Yanai, J., Zhao, F.J., McGrath, S. and Kosaki, T. 2006: Effect of soil characteristics on Cd uptake by the hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens. Environmental Pollution, 139, 167-175.
26. Itami, K. and Yanai, J. 2006: Sorption and desorption properties of cadmium and copper on soil clays in relation to charge characteristics. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 52, 5-12.
27. Sano, S., Yanai, J. and Kosaki, T. 2006: Relationship between labile organic matters and nitrogen mineralization in Japanese agricultural soils with reference to land use and soil type. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 52, 49-60.
28. Imamura, A., Yumoto, T. and Yanai, J. 2006: Urease activity in soil as a factor affecting the succession of ammonia fungi. Journal of Forest Research, 11, 131-135.
29. Funakawa, S., Yanai, J., Hayashi, Y., Hayashi, T., Watanabe, T., Noichana, T., Panitkasate, T., Katawatin, R., Kosaki, T. and Nawata, E. 2006: Soil organic matter dynamics in a sloped sandy cropland of northeast Thailand with special reference to the spatial distribution of soil properties. Japanese Journal of Tropical Agriculture, 50, 199-207.
30. Yanai, J., Nakata, S., Funakawa, S., Nawata, E., Katawatin, R., Tulaphitak, T. and Kosaki, T. 2007: Evaluation of nutrient availability of sandy soil in northeast Thailand with reference to growth, yield and nutrient uptake by maize. Japanese Journal of Tropical Agriculture 51, 169-176.
31. Takata, Y., Funakawa, S., Yanai, J., Mishima, A., Akshalov, K., Ishida, N., and Kosaki, T. 2008: Influence of crop rotation system on the spatial and temporal variation of the soil organic carbon budget in northern Kazakhstan. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 54, 159-171.
32. Liu, M.Q., Yanai, J., Jiang, R.F., Zhang, F. McGrath, S.P. and Zhao, F.J. 2008: Does cadmium play a physiological role in the hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens? Chemosphere, 71, 1276-1283.
33. Matsui, N., Suekuni, J., Havanod, S., Nishimiya, A., Yanai, J. and Kosaki. T. 2008: Determination of soil-related factors controlling initial mangrove (Rhizophora apiculata BL.) growth in an abandoned shrimp pond. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 54, 301-309.
34. Yanai, J., Noguchi, J., Yamada, H., Sugihara, S., Kilasara, M. and Kosaki, T. 2009: Function of geophagy as supplementation of micronutrients in Tanzania. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 55, 215-223.
35. Meharg, A.A., Williams, P.N., Adamako, E., Lawgali, Y.Y., Deacon, C., Villada, A., Cambell, R.C.J., Sun, G., Zhu, Y.G., Feldmann, J., Raab, A., Zhao, F.J., Islam, R., Hossain, S. and Yanai, J. 2009: Geographical variation in total and inorganic arsenic content of polished (white) rice. Environmental Science and Technology, 43, 1612-1617.
36. Yamada, H., Kamada, A., Usuki, and Yanai, J. 2009: Total selenium content of agricultural soils in Japan. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 55, 616-622.
37. Moritsuka, N., Matsuoka, K., Matsumoto, S., Masunaga, T. and Yanai, J. 2010: Significance of plant-induced solubilization of soil nitrogen: A case of komatsuna plants grown in fertilized soils. Plant Production Science, 13, 307-313.
38. Yanai, J., Nakata, S., Funakawa, S., Nawata, E., Katawatin, R. and Kosaki, T. 2010: Effect of NPK application on the growth, yield and nutrient uptake by sugarcane on a sandy soil in northeast Thailand. Tropical Agriculture and Development, 54, 113-118.
39. Yanai, J., Yamada, K. Yamada, H., Nagano, Y. and Kosaki, T. 2011: Risk assessment of heavy metal-contaminated soils with reference to the aging effect. Pedologist, 54, 278-284.
40. Yanai, J., Okada, T., and Yamada, H. 2012: Elemental composition of agricultural soils in Japan in relation to soil type, land use and region. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 58, 1-10.
41. Ogasawara, S., Nakao, A. and Yanai, J. 2013: Radiocesium interception potential (RIP) of smectite and kaolin reference minerals containing illite (micaceous mineral) as impurity. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 59, 852-857.
42. Nakao, A., Ogasawara, S., Sano, O., Ito, T. and Yanai, J. 2014: Radiocesium sorption in relation to clay mineralogy of paddy soils in Fukushima, Japan. Science of the Total Environment, 468-469, 523-529.
43. Yanai, J., Ohmoto, T., Nakao, A., Koyama, K., Hartono, A. and Anwar, S. 2014: Evaluation of nitrogen status of agricultural soils in Java, Indonesia. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 60, 188-195.
44. Moritsuka, N. Matsuoka, K. Katsura, K. Sano, S. and Yanai, J. 2014: Soil color analysis for statistically estimating total carbon, total nitrogen and active iron contents in Japanese agricultural soils. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 60, 475-485.
45. Yanai, J., Mizuhara, S. and Yamada, H. 2015: Soluble selenium content of agricultural soils in Japan and its determining factors with reference to soil type, land use and region. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 61, 312-318.
46. Nakao, A., Takeda, A., Ogasawara, S., Yanai, J., Sano, O. and Ito, T. 2015: Radiocesium interception potential of paddy soils in Fukushima, Japan, in relation to selected physicochemical properties. Journal of Environmental Quality, 44, 780-788.
47. Moritsuka, N., Katsura, K., Matsuoka, K. and Yanai, J. 2015: Decadal sustainability of spatial distributions of soil properties in a paddy field as a fingerprint reflecting soil forming factors and field managements. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 61, 516-527.
48. Hartono, A., Anwar, S., Satwoko, A., Koyama, K., Omoto, T., Nakao, A. and Yanai, J. 2015: Phosphorus fractions of paddy soils in Java, Indonesia. Journal of International Society for Southeast Asian Agricultural Sciences, 21-2, 20-30.
49. Nakao, A., Nakao, A., Tanaka, R., Ogasawara, S. and Yanai, J. 2015: Aeolian-dust-derived micaceous minerals control radiocesium retention in Andosols in Japan. Soil Science Soceity of America Journal, 79, 1590-1600.
50. Yanai, J., Taniguchi, H. and Nakao, A. 2016:Evaluation of available silicon content and its determining factors of agricultural soils in Japan. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 62, 511-518.
( May, 2017 )
![]()
